Designing a NN Algorithm
Let's Design a NN Algorithm!
Let's revisit the salmon and bass classification example! Recall the problem of classifying an unknown sample:

Question:
Let's say that, for our classification algorithm, you want to assume the unknown fish and "closest" or "most similar" fish share the same classification label. How can you calculate this? Hint: Which fish is the most similar to our unknown fish? How did you come to this conclusion?
Answer:
You may have said that, visually, the most similar fish is the one with the shortest physical distance on the graph to the unknown fish. Let's use this idea to make an algorithm for obtaining the most similar fish!
If you are trying to find the fish closest to our unknown fish on the graph, you want to minimize the distance between the points. You can find the distance between any fish and our unknown fish by calculating the Euclidean distance between the points:
where represents a fish's width and represents a fish's length. Using this equation, you can calculate the distance between every fish and the unknown fish. Then, you can choose the closest fish by determining the fish with the shortest distance to the unknown fish. Finally, you can assign the unknown fish's label to be equal to the closest fish's label with the following steps:
- Calculate the distance between the unknown fish and every fish in the training dataset
- Find the shortest distance for all calculated distances
- Find the fish that corresponds to this distance
- Find the label that corresponds to this fish
- Set this label to be our unknown fish's label
Using this algorithm, the closest fish found is the following:
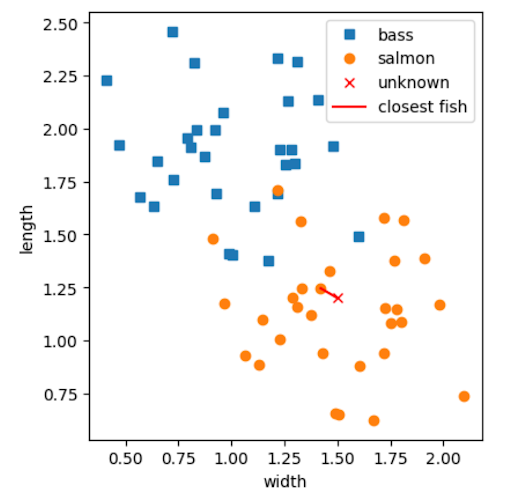
As a result, the unknown fish can be classified as a salmon. You've built your first k-NN classifier! Congratulations!

